Explore the causes of dental implant infections and discover effective remedies in this informative guide. Whether you have dental implants or are considering them, learn how to maintain a healthy, radiant smile by understanding, preventing, and addressing potential issues.
Recognizing an Infected Implant
Recognizing an infected implant can be critical for your health and well-being, as infections around implants can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Implants can include medical devices like joint replacements, pacemakers, and dental implants, or cosmetic implants like breast or facial implants. Here are some common signs and symptoms that may indicate an infected implant:
- Pain: Persistent, increasing, or unexplained pain around the implant site can be a significant indicator of infection.
- Swelling: Swelling and inflammation around the implant site can be a sign of infection. It may also feel warm to the touch.
- Redness: The skin over the implant may become red or discolored. Redness spreading from the implant site is a concerning sign.
- Fever: A fever is a systemic sign of infection. If you develop a fever without any other apparent cause, it may be related to the implant.
- Drainage or Pus: If you notice any discharge or pus coming from the implant site, it is a clear sign of infection.
- Increased Sensitivity: An increase in sensitivity or tenderness around the implant may indicate an issue.
- Change in Function: Changes in the function of the implant may also be a sign of infection. For example, if a joint replacement becomes difficult to move or a pacemaker is not functioning correctly, infection may be the cause.
- General Malaise: Feeling generally unwell, fatigued, or experiencing other systemic symptoms can be an indication of an implant infection.
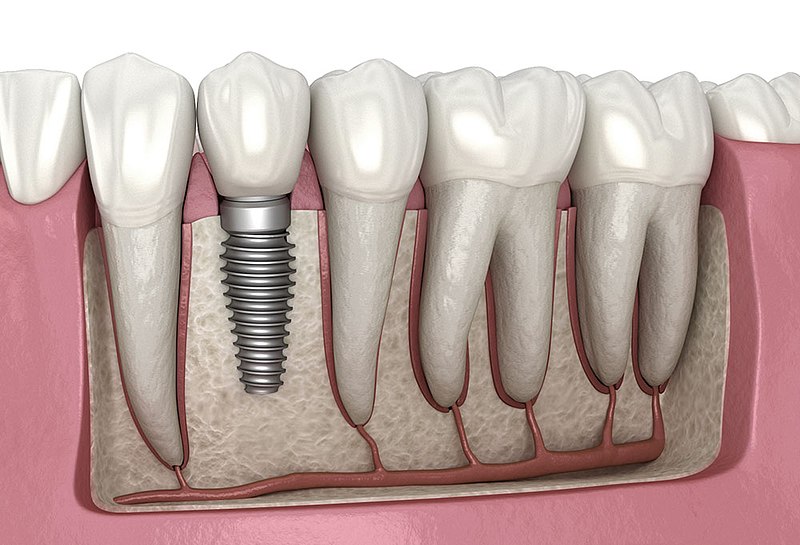
Why are dental implants infected?
Dental implants can become infected due to various factors, just like any other surgical procedure carries a risk of infection. Infection around a dental implant is known as peri-implantitis. The following factors contribute to the risk of dental implant infections:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: One of the most significant risk factors for dental implant infection is inadequate oral hygiene. If a patient doesn’t maintain proper oral care, plaque and bacteria can accumulate around the implant, leading to infection. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining oral health around implants.
- Smoking: Smoking is associated with a higher risk of dental implant infections. It can impair the body’s ability to heal and fight off infections.
- Compromised Immune System: Patients with compromised immune systems due to conditions like diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or medications like corticosteroids are at a greater risk of infections following dental implant surgery.
- Gum Disease (Periodontitis): Pre-existing gum disease can increase the risk of implant infections. Bacteria from periodontitis can spread to the implant site, causing infection.
- Inadequate Bone Support: Dental implants need a sufficient amount of healthy bone to integrate properly. If there is insufficient bone support, it can lead to complications, including infections.
- Uncontrolled Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can slow down the healing process, making the patient more susceptible to infections.
- Dental Implant Placement Issues: If the dental implant is placed improperly, it can create spaces where bacteria can accumulate, leading to infection. It is crucial that the implant is placed correctly by a skilled oral surgeon or periodontist.
- Prosthesis Issues: Problems with the implant’s prosthesis, such as an ill-fitting crown or bridge, can cause food and bacteria to accumulate, increasing the risk of infection.
- Foreign Body Reaction: Some individuals may have a heightened sensitivity to the implant materials (usually made of titanium). This sensitivity can lead to chronic inflammation and, in some cases, infection.
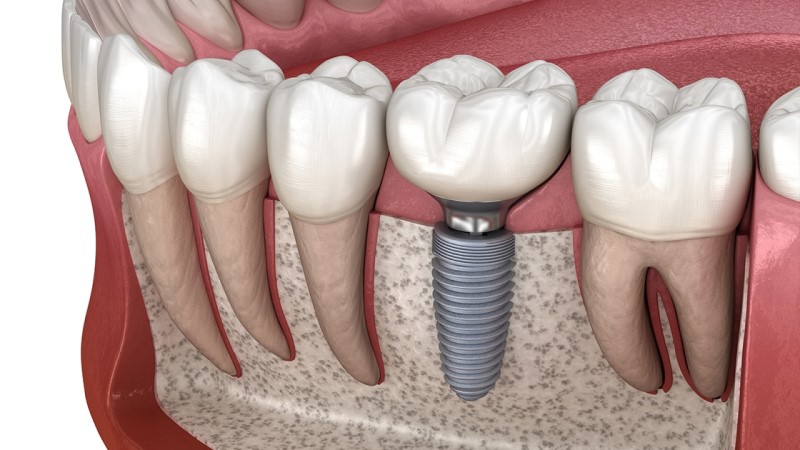
Treating Dental Implant Infections
Treating dental implant infections, also known as peri-implantitis, is crucial to prevent further complications and potential implant failure. The treatment approach for implant infections may vary depending on the severity of the infection, but here are some common steps and options involved in managing dental implant infections:
- Professional Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planning): In the early stages of peri-implantitis, your dentist or periodontist may perform a professional cleaning procedure similar to scaling and root planning, which is used to treat gum disease. This involves removing plaque and calculus (tartar) from the implant’s surface and the surrounding tissues.
- Antibiotics: If the infection is localized and not too severe, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to help combat the infection. This can be particularly effective when used in combination with other treatments.
- Surgical Debridement: For more advanced cases of peri-implantitis, surgical debridement may be necessary. During this procedure, the infected tissue is removed, and the implant surface is cleaned to promote healing. It may also involve bone grafting to restore lost bone support.
- Laser Therapy: Some dental professionals use laser therapy to treat peri-implantitis. Lasers can help remove infected tissue and bacteria while promoting healing.
- Regenerative Procedures: In cases where bone loss has occurred around the implant, regenerative procedures such as bone grafting or guided tissue regeneration may be necessary to rebuild and support the lost bone tissue.
- Implant Removal: In severe cases where the infection cannot be controlled or if the implant is significantly compromised, the implant may need to be removed to prevent further complications. Once the infection is resolved, a new implant may be considered after the area has healed.
- Oral Hygiene Improvement: Patients are typically advised to improve their oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and the use of antimicrobial mouth rinses. Your dental care provider may also recommend more frequent dental check-ups and cleanings.
Conclude
In conclusion, this overview highlights the importance of understanding the causes of dental implant infections and the effective remedies available. We discussed the recognition of infected implants, explored the underlying reasons for implant infections, and delved into the various treatment options. It is crucial for both patients and dental professionals to be well-informed about these aspects in order to prevent, identify, and address dental implant infections effectively.


