Things to Know About Core Build Up Dental Procedures
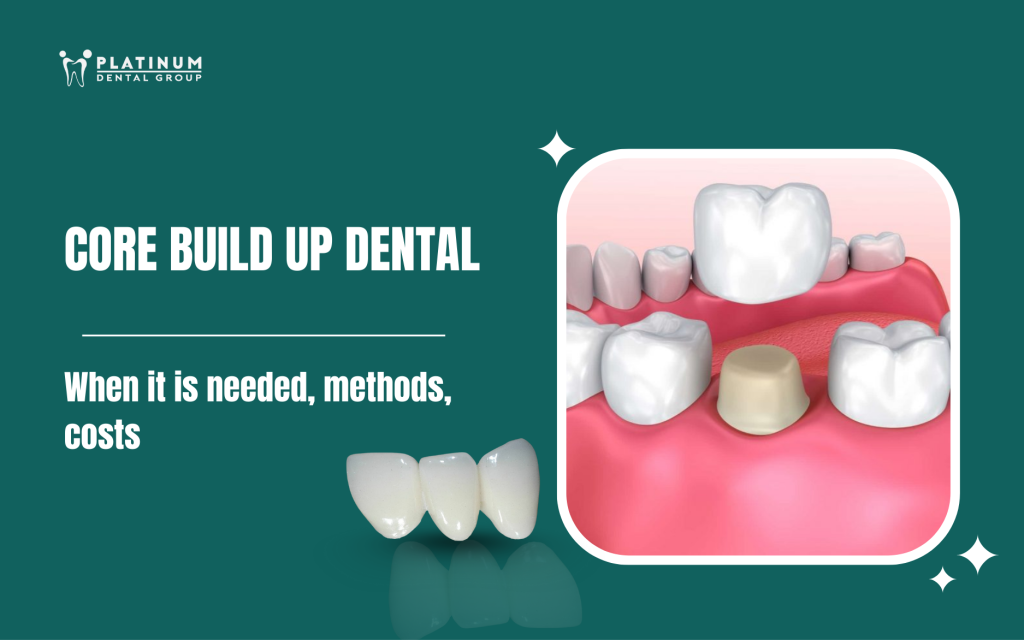
Core build up dental is a crucial step in prosthodontics aimed at restoring the lost part of the tooth body, helping the tooth become stable enough to support a porcelain crown and maintain stable chewing function. This technique is indicated in many cases such as large fractures, severe decay, teeth after root canal treatment, or when there is not enough tooth tissue left to hold a crown. Understanding what core build-up is, when it needs to be done, and current methods will help you be more proactive in the treatment process. The article below provides detailed, accurate, and easy-to-understand information to help you easily choose the right solution, ensuring long-term oral health.
Nội dung bài viết
- 1 What is core build up dental?
- 2 When is it necessary to perform core build up dental?
- 3 Current core build up dental methods
- 4 Materials for core build up dental
- 5 Core build up dental procedure at the dental clinic
- 6 How much does core build up dental cost?
- 7 Where to get good core build up dental treatment?
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
What is core build up dental?
Core build up dental is a restorative technique aimed at rebuilding the lost or missing part of the tooth body, helping to create a solid pillar (abutment) to support a porcelain crown. When the natural tooth tissue is no longer sufficient to hold a crown, the dentist will use materials such as composite or place a post into the root canal to reconstruct the tooth form. This technique helps the tooth have a standard shape, withstand force well, and be ready for the porcelain crown covering the outside.

Core build up dental is usually indicated in the following cases:
- Large fractures or broken tooth body: The remaining tooth tissue is too little to hold a porcelain crown.
- Severe decay, recurrent decay: The tooth structure is heavily destroyed and cannot be filled with standard methods.
- Teeth after root canal treatment: Teeth are often weaker and more brittle, needing reinforcement with a post or a composite build-up block.
- Chipped or heavily worn teeth: Not enough tissue surface to proceed with safe crowning.
In these cases, if the core is not rebuilt, the porcelain crown is very easy to loosen, fall out, or cause root fracture during chewing.
See also: General information related to tooth Implant
Distinguishing core build up dental from normal fillings
Dental filling is a technique to restore small to medium damage on the tooth surface, mainly to fill cavities or cover lost enamel and dentin. The filling material is attached directly to the tooth and does not have the task of creating a supporting pillar. Meanwhile, core build up dental is indicated when the tooth body is lost too much, and the remaining tooth tissue is not enough to hold a porcelain crown. At this time, the dentist needs to reconstruct the tooth shape using composite or a post-core to create a solid foundation before full porcelain restoration.
Distinguishing core build up dental from dental crowns
Core build-up and dental crowns are two different steps in the restoration process. Core build-up is the stage of remaking the lost tooth body, creating a fixed pillar to support the crown. Crowning is the next step, using a porcelain crown to cover the entire core to restore aesthetics and chewing function. In other words, core build-up helps “prepare the foundation,” while crowning is the finishing part, bringing a natural look and long-term durability.
See also: General information about the cost of full mouth Dental Implants
When is it necessary to perform core build up dental?
Core build up dental is indicated when natural tooth tissue is no longer sufficient to support a porcelain crown or cannot withstand force on its own during chewing. Each situation below carries a risk of tooth fracture, crown loss, or reduced lifespan of the restoration if the core is not rebuilt at the right time.
Teeth with large fractures, not enough tissue to hold a porcelain crown
When a tooth is traumatized, has a large corner break, or a broken body, the remaining tissue is usually not enough to firmly attach a porcelain crown. If core build-up is skipped, the porcelain crown will easily loosen, shift, or pop out when chewing. More seriously, chewing force can cause vertical root fractures, making the tooth unpreservable and forcing extraction.
Severe decay or recurrent decay
In teeth with large decay, extensive decay, or recurrent decay after filling, the natural tooth tissue has been heavily destroyed and no longer has the ability to withstand force. If the tooth body structure is not recreated, the porcelain crown cannot adhere firmly, and the risk of pulpitis, tooth cracking, or tooth fracture in the future is very high. Core build up dental ensures the tooth has a solid foundation before entering restoration.
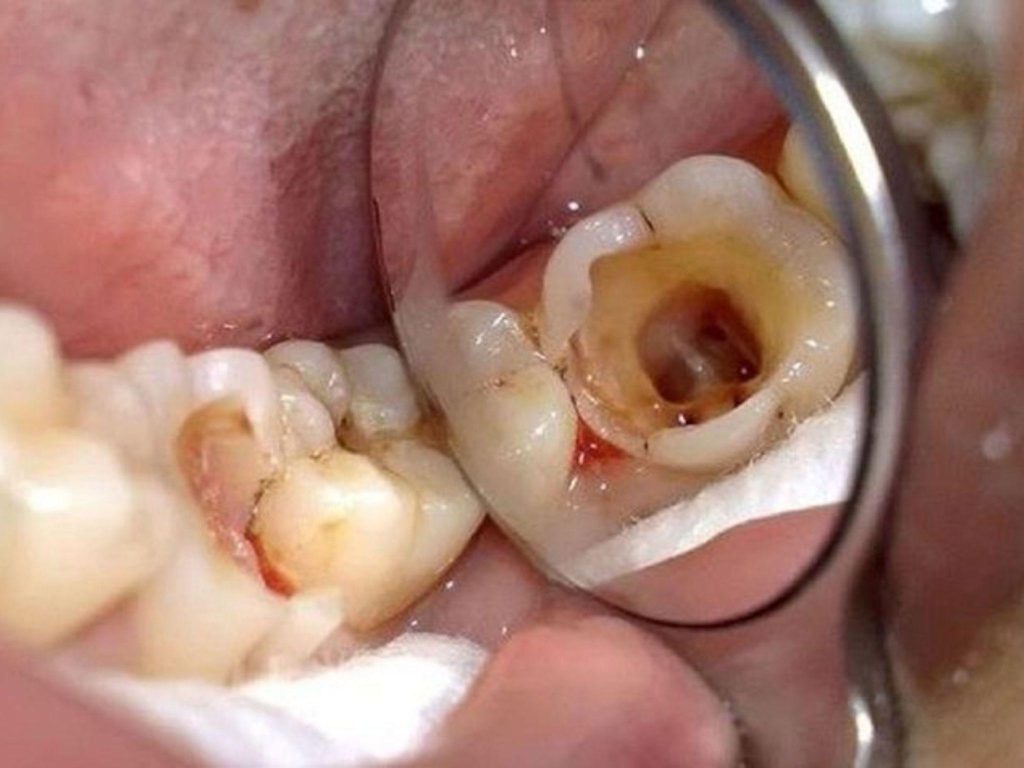
Teeth after root canal treatment are weak, brittle, and easy to break
After removing the pulp, the tooth loses its nourishment, so it becomes more brittle and easily breaks under the impact of chewing force. Core build-up using composite or fiberglass posts helps reinforce the entire tooth body, increasing load-bearing capacity and reducing the risk of horizontal fractures at the gum line. If not performed, a tooth after root canal treatment can break suddenly and cannot be saved.
Teeth after root canal treatment are weak, brittle, and easy to break
After removing the pulp, the tooth loses its nourishment, so it becomes more brittle and easily breaks under the impact of chewing force. Core build-up using composite or fiberglass posts helps reinforce the entire tooth body, increasing load-bearing capacity and reducing the risk of horizontal fractures at the gum line. If not performed, a tooth after root canal treatment can break suddenly and cannot be saved.
Teeth with severe enamel erosion
Enamel erosion due to grinding, improper brushing, or acid erosion can cause teeth to be short, small, and no longer have enough height to be ground into a core for crowning. Not rebuilding the tooth body makes the porcelain crown unable to be fixed and easily slip off in a short time. Core build-up helps restore the height of the tooth body, creating conditions for the porcelain crown to adhere firmly and distribute chewing force reasonably.
Current core build up dental methods
Depending on the amount of remaining tooth tissue, pulp condition, and restoration requirements, the dentist will choose the appropriate core build-up method. Below are the techniques commonly used in dentistry today.
Core build up dental using Composite
Core build-up using composite is applied when the tooth still has a part of the body sufficient for the material to adhere to. Composite has a color similar to real teeth and is easy to shape, making it suitable for cases of moderate fractures or tissue loss that is not too deep.
- Advantages: The implementation process is fast, cost-effective, and brings relatively good aesthetics.
- Disadvantages: The durability of composite is lower than that of a post-core, and it is easy to wear or peel if subjected to strong chewing force. Therefore, this method is usually suitable for teeth that do not have to withstand excessive force.
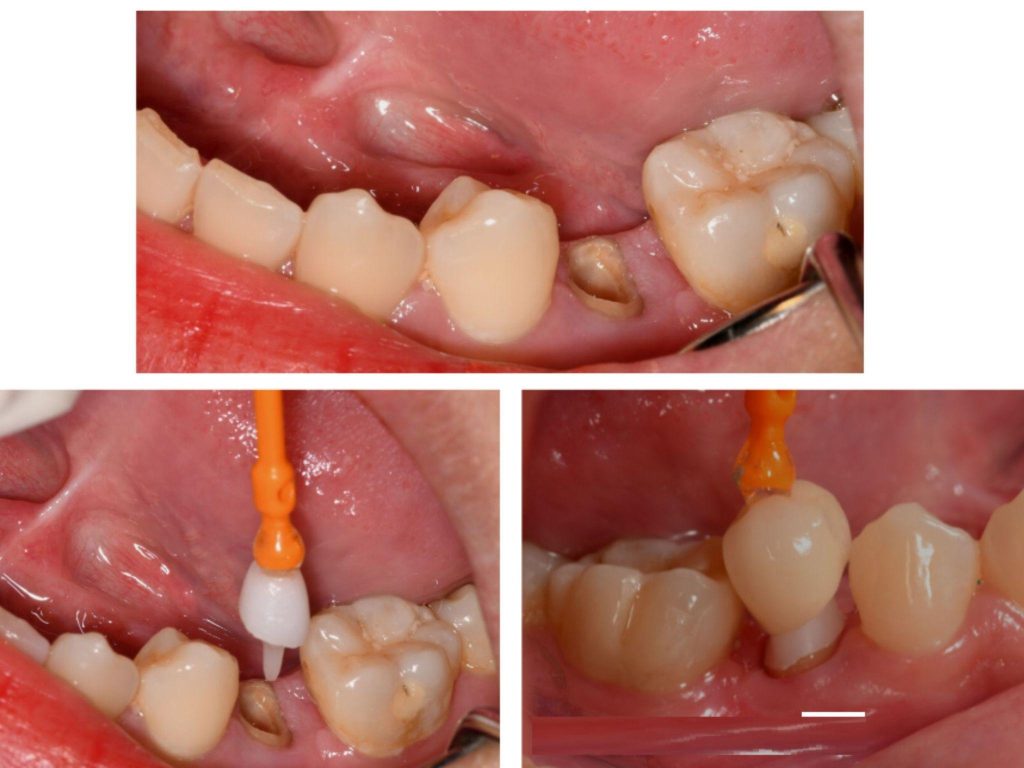
Core build up dental using a Post (Post-core)
In teeth with significant tissue loss, especially teeth after root canal treatment, rebuilding the core with composite alone is not stable enough. At that time, the dentist will place a post into the root canal to fix the false core, helping the tooth have a solid supporting pillar before crowning.
Common types of posts include:
- Fiberglass post: High aesthetics, elasticity close to real teeth, reducing the risk of root fracture. Often prioritized for incisors or positions requiring aesthetics.
- Metal post: Very high durability, good load-bearing, suitable for molars. However, it can cause a slight gray shadow at the tooth neck or transmit force more strongly, increasing the risk of root fracture in some cases.
The post-core build-up method is suitable for cases of large fractures, very little remaining tooth body, or teeth after root canal treatment needing reinforcement.
Core build-up technique combined with all-ceramic crowns
The core build-up technique combined with all-ceramic crowns is a comprehensive solution for weak teeth, significant tissue loss, or the need to restore both aesthetics and function simultaneously. The process involves rebuilding the tooth body with composite or a post-core, then covering it with an all-ceramic crown to protect the entire internal structure. The core build-up technique combined with all-ceramic crowns helps ensure the tooth has stable durability, reasonable chewing force distribution, and achieves high aesthetics, especially in the incisor area.
Materials for core build up dental
In core build up dental, materials are selected based on the extent of tooth tissue loss, load-bearing requirements, and the subsequent restoration plan. Each type of material possesses its own pros and cons, helping dentists make the most suitable choice for each case.
Dental Cement for core build-up
Dental cement used to be commonly used to rebuild the lost tooth body. This material has the ability to harden quickly, adhere relatively well to tooth tissue, and withstand force at a basic level. However, today cement is less used because of limited durability and low aesthetics. They are usually only used in temporary cases or simple restorations.
Amalgam
Amalgam is a mixed metal material with high hardness and durability. Thanks to its good load-bearing capacity, amalgam used to be used in core build-up for molars. However, the characteristic metal color makes this material unsuitable for positions requiring aesthetics or combined with all-ceramic crowns. Besides, amalgam can cause discoloration of tooth tissue, so currently, it is no longer prioritized in aesthetic restoration.

Composite
Composite is the most popular restorative material today thanks to good aesthetics, easy shaping, and good adhesion to tooth tissue. Composite is suitable for core build-up in teeth that still have relatively substantial tissue, moderate fractures, or teeth needing a slight lift of the body before crowning. The disadvantage is limited load-bearing capacity, so with teeth that have lost too much tissue or teeth after root canal treatment, composite often must be combined with a post-core.
Cast Metal
Cast metal is used in the post-core system for teeth requiring very sturdy supporting pillars. This material has high durability, withstands force well, and is suitable for molars or teeth with almost total tissue loss. However, the disadvantage lies in low aesthetics and the potential to cause a slight dark shadow at the tooth neck. Therefore, cast metal is usually indicated in the posterior tooth region, where high load-bearing is required.
Core build up dental procedure at the dental clinic
The core build up dental procedure is performed according to standard steps to ensure the durability of the core, the ability to hold the crown, and safety throughout the treatment process. Depending on the condition of each tooth, the dentist may adjust the technique, but generally, it includes the following steps:
Examination – X-ray to determine remaining tooth tissue
The doctor conducts an overall oral check, assessing the degree of fracture, decay, or wear of the tooth. X-rays help determine the condition of the tooth root, the length of the root canal, and the amount of remaining tooth tissue to choose the appropriate core build-up method. This is an important step to ensure safe, accurate core reconstruction without affecting the tooth root.
Root Canal Treatment (if necessary)
In teeth with large decay, fractures reaching the pulp chamber, or signs of pulpitis, the doctor will indicate root canal treatment before reconstruction. This helps remove inflamed pulp tissue, avoid pain, and protect the tooth long-term. In some cases where the tooth still has a healthy pulp and the damage does not affect the pulp chamber, this step is not needed.
Placing a post or applying composite to rebuild the tooth body
The goal of this step is to create a solid pillar with the correct standard shape to support the porcelain crown. Based on the extent of tooth tissue loss, the doctor advises on choosing the appropriate method.
- Tooth with sufficient tissue: The doctor uses composite to build up and recreate the tooth body shape.
- Tooth with significant tissue loss or post-RCT: The doctor places a post (post-core) into the root canal, then builds the core outside using composite or cast metal.
Grinding the core and taking impressions for crowning
After the core is completely reconstructed, the doctor grinds and adjusts the shape to create space for the porcelain crown. Next, taking impressions is performed using 3D scanning technology or traditional impression trays to fabricate a porcelain crown that fits the core perfectly.
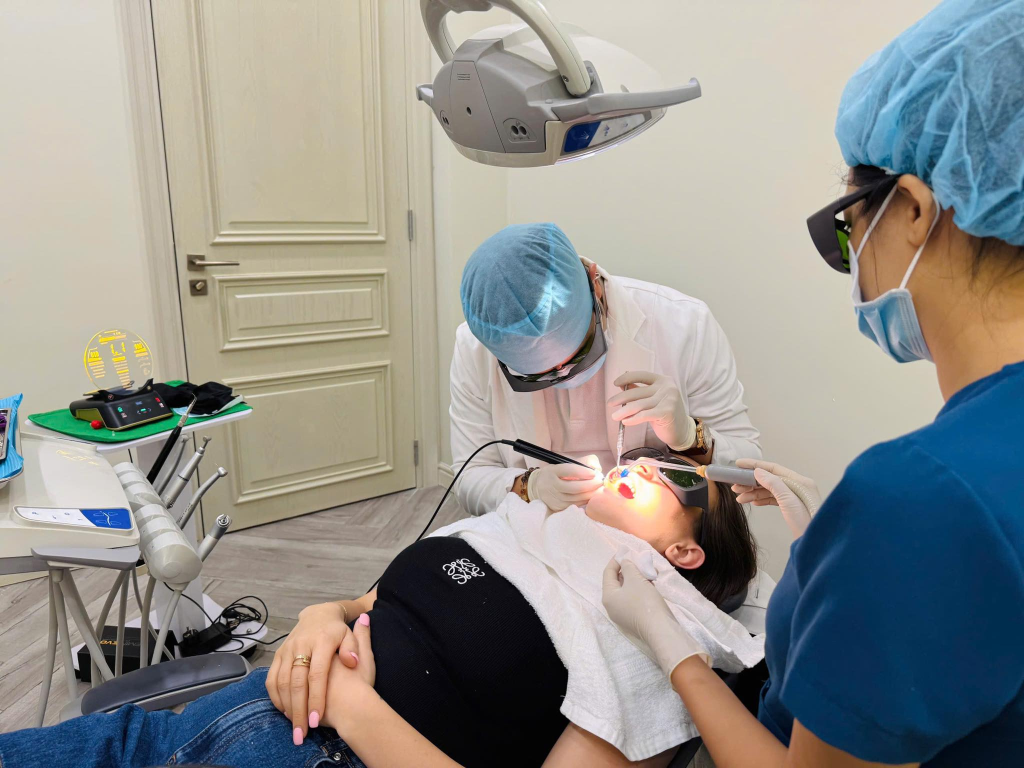
Attaching the finished porcelain crown
When the porcelain crown is fabricated, the doctor tries the crown on the core to check the fit, bite, and color. If all factors meet the standard, the crown will be permanently attached using specialized dental cement. Ending this process, the restored tooth can chew stably and has natural aesthetics.
How much does core build up dental cost?
The cost of core build up dental depends on the implementation method, materials used, and the condition of the remaining tooth tissue. Prices between dental clinics may vary but generally fluctuate within a reasonable range, suitable for many treatment needs.
The table below helps you visualize the cost for each core build-up technique:
| Core Build Up Dental Method | Reference Cost (VND/tooth) | Note |
| Core build-up with Composite | 300,000 – 800,000 | Suitable for teeth with ample tissue, moderate fractures, no post needed. |
| Core build-up with Fiberglass Post (Post-Core) | 1,000,000 – 2,500,000 | Good aesthetics, suitable for teeth after root canal treatment or large tissue loss. |
| Core build-up with Metal Post/Cast Metal | 800,000 – 2,000,000 | High durability, usually used for molars; less aesthetic than fiber posts. |
Costs may change depending on material quality, the complexity of each case, and the technology used at each dental clinic. In cases where the tooth needs root canal treatment or a crown after reconstruction, the total cost will be calculated according to each separate category.
Where to get good core build up dental treatment?
Core build up dental is a technique that requires doctors to have high expertise in prosthodontics and endodontics, the ability to assess prognosis, and choose suitable materials for each case. Therefore, choosing the right reputable dental clinic directly determines the durability of the restoration, aesthetics, and the ability to preserve real teeth in the long term.
When needing core build up dental for porcelain crown restoration, many customers choose Platinum Dental Group thanks to solid medical expertise, international standard treatment processes, and a philosophy of maximum tooth preservation. Here, all core build-up cases are performed by experienced prosthodontic-endodontic doctors, helping to accurately assess the amount of remaining tooth tissue, choose suitable materials, and strictly control the risk of body fracture or root fracture.

At Platinum Dental Group, customers can rest assured thanks to:
- Doctors specialized in prosthodontics and aesthetic porcelain: Perform core build-up using microsurgical techniques, precise manipulation to optimize the adhesion and durability of the porcelain crown.
- 100% Digital Diagnosis: CT ConeBeam imaging, endodontic microscope, intraoral scanning to clearly define tooth structure before reconstruction.
- High-end, durable materials: Nano composite and imported fiberglass posts help the restored tooth body be sturdy, withstand force well, and limit the risk of vertical fracture.
- Porcelain crowns fabricated by CAD/CAM: Ensure the crown hugs the reconstructed core tightly, increasing the lifespan of the restoration and ensuring maximum aesthetics.
- International standard sterile process: Absolutely safe for root-canal-treated teeth or weak tooth tissue.
- Transparent warranty policy: Helps customers feel secure throughout the usage process.
If your tooth is heavily broken, partially fractured, weak after root canal treatment, or does not have enough tooth tissue to crown, early examination at Platinum Dental will help preserve the real tooth as much as possible and avoid the risk of extraction.
See also: General information about full mouth Dental Implants near me
Frequently Asked Questions
Is core build up dental as durable as a real tooth?
The durability of the reconstructed dental core depends on the implementation technique, materials, and remaining tooth tissue. Although it cannot be 100% as durable as a real tooth, a reconstructed core still achieves high hardness and stability when done according to the correct indication and covered with a standard porcelain crown.
Does core build up dental hurt?
The core build up dental process usually does not cause pain, because the doctor will administer local anesthesia. Afterward, you may feel slight sensitivity for 1-2 days, which will stabilize quickly if cared for according to instructions.
Is core build up dental dangerous?
Core build up dental is a safe, minimally invasive technique commonly used in restorative dentistry. Risks only occur if low-quality materials are used or manipulation is not standard, so you should have it done at a reputable dental clinic.
How long does a core build up dental last?
The maintenance time is usually from 5-10 years, or even longer if the tooth is well restored with a crown, has a stable bite, and proper oral care.
Does core build up dental turn black?
Reconstruction using composite or fiberglass posts almost never turns the tooth black. Only some old techniques using metal posts carry a risk of affecting color if the tooth is too thin or the porcelain crown does not cover well.
Can a tooth decay again after reconstruction?
The tooth can still decay again if bacteria invade the remaining natural tooth tissue. Poor hygiene or an open crown margin can lead to recurrent decay. Periodic re-examination will help detect and handle it early.
Can core build up dental be done multiple times?
It can be redone if the old material peels, breaks, or the porcelain crown needs replacement. However, each reconstruction depends on the amount of remaining natural tooth tissue, so careful assessment by a doctor is needed.
Can the core build up dental fall out?
A reconstructed dental core rarely falls out if good materials are used and attached with the correct technique. In cases where the tooth has too little tissue left, the doctor may indicate placing a fiberglass post to increase stability.
Core build up dental is an important step helping to restore teeth that have lost a lot of tissue and create a solid foundation before crowning. When performed according to the correct indication and technique, the tooth will achieve good durability, stable chewing, and maximize the limitation of fracture risks later. If you are experiencing weak teeth, large decay, heavy breakage, or post-root canal conditions, early examination will help the doctor provide a suitable restoration direction and save the most costs.
If you need more detailed advice or want to check your current tooth condition, you can visit Platinum Dental Group to be examined by a doctor and given a clear regimen. Direct assessment will help you understand exactly if you need core build up dental and choose the safest solution for your oral health.
Learn more:
- General information about Veneer teeth
- General information about Dental Crown treatment
- Important information about all on 4 Dental Implants near me
Platinum Dental Group
Clinic Locations:
📍Platinum Dental Central: 127 Nguyen Cu Trinh Street, Cau Ong Lanh Ward, Ho Chi Minh City
📍Platinum Dental Thao Dien: 1H Street 10, An Khanh Ward, Ho Chi Minh City
📞 Hotline: (+84) 28 3920 9969 | 096 779 7799
✉️ Email: info@platinumdentalvietnam.com
🌐 Website: https://platinumdentalvietnam.com/
💬 Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/platinumdental.vietnam/
🔗 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/platinumdentalvn



 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt